






Bond Measures E and H,
passed in 1998, provided funds for much-needed renovation and modernization of
schools within the Santa Cruz City Schools District. Overall, the
The
Alternate: an optional component of a construction project
BAN: Bond
Anticipation Note; a note issued in anticipation of later issuance of bonds,
usually payable from the proceeds of the sale of the bonds anticipated
BOC: Santa Cruz City Schools Bond Oversight Committee
California Code of
Regulations (CCR), Title 24: also known as the California Building
Standards Code. Public school construction in
Change Order: a written order that modifies the plans, specifications, or price of a signed construction contract agreement. Change orders can be initiated for a variety of reasons, including unforeseen conditions, owner-requested changes, design errors or omissions, contractor error, and weather-related problems during construction.
DSA: Division of the State Architect
DSA
Form-5: the official DSA form that
details the project inspector’s qualifications
IOR: Inspector of Record; a state-certified inspector that performs state-mandated site inspection services for public school construction and who is hired and paid by the owner (school district)
Multiple-prime contracting: the owner (school district) holds separate contracts with contractors of various disciplines (such as general, mechanical, electrical). The owner, or its construction manager, manages the overall schedule and budget during the entire construction phase.
RFP: Request for Proposal; an invitation to bid, or a proposal inviting bids from possible suppliers of a product or service
SB50: the 1998 state bond measure that provided matching funds to the Santa Cruz City Schools District for modernization projects. District matching funds were generated from Bond Measures E and H.
SCCS: Santa Cruz City Schools
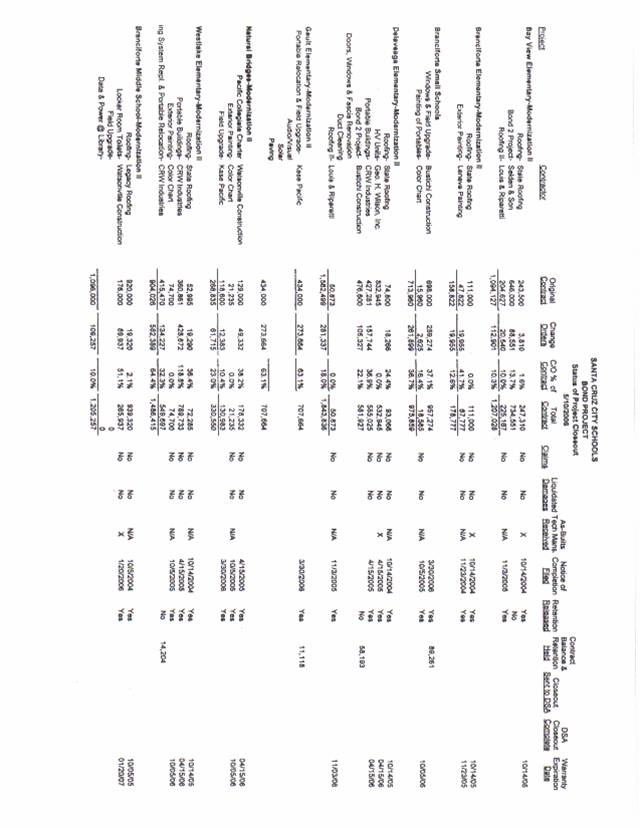
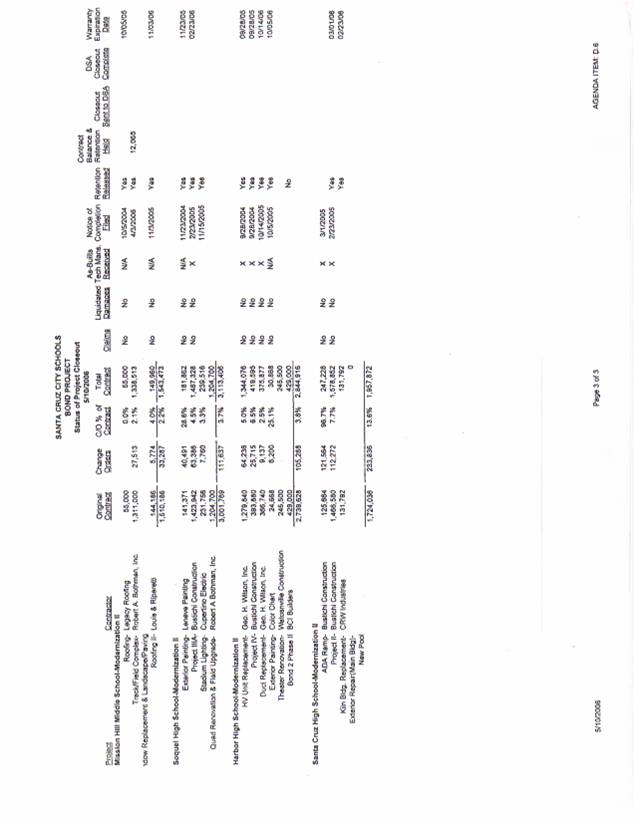
SCCS Bond Project,
Status of Project Closeout,
Stop Notice: a notice to withhold payment from a
contractor and to set money aside to satisfy a claim
In April 1998, voters in the Santa Cruz City Schools (SCCS) District passed two bond measures worth a total of $86 million. The district spent over $300,000 for this special election for Measure E and Measure H that was held just seven weeks prior to the regularly scheduled June primary election.[1]
Measure E, approved by seventy-nine percent (79%) of the voters, was for elementary school improvements not to exceed $28 million, and Measure H, approved by seventy-four percent (74%) of the voters, was for junior and senior high school improvements not to exceed $58 million. The measures stated that the bond money would be used to rehabilitate the schools, including replacing inadequate electrical, plumbing, heating, and window systems; to comply with fire, earthquake, health, safety, and accessibility standards; and to renovate, construct, and modernize classrooms, restrooms, and other school facility improvements. Bond money would not be used for administrator salaries. Expenditures would be monitored by a community bond oversight committee, with all proceeds spent to benefit district schools. All elementary and secondary school sites in the district were included in the bond measures.
Voter Information Pamphlet arguments in favor of
Measures E and H stated that “By law, absolutely none of the funds raised by
these ballot measures can be used for administrative salaries, offices, or
operating expenses. All of the funds raised by these measures will stay in our
local community and will be used to fix our schools.”[2]
The E and H bonds were originally each sold in three series:
A, B, and C. Series A was sold in 1998, Series B in 2000, and Series C in 200l. According
to the Voter Information Pamphlet, “Impartial Analysis by
As each series was sold, the money from the sale
was deposited into the Santa Cruz County Treasury to be withdrawn by the Santa
Cruz City Schools District as needed for the bond projects. As property taxes
are collected, they are also deposited in the
The Santa Cruz County Assessor’s Office establishes the rate that each property owner in the Santa Cruz City Schools District must pay toward the bonds. For the tax year 2005-2006, the rate is:[3]
At this rate, taxes resulting from Bond Measures E and H on
property within the City of
The school renovation projects were not funded solely by the
proceeds of bonds E and H sales. Under the State Construction Program, the
district applied in 1999 for SB50 (State Bond 50) funds for modernization that
it began receiving in July 2000. These state funds were earmarked for
renovation of schools that met the age requirement for modernization
(twenty-five years or older). This was a cash-matching program, and E and H
funds were used for the match. The district received over $28 million from the
state. Additions including bond interest, developer fees, deferred maintenance
funds, and donations brought the total revenue for bond projects to
$128,683,715 as of
|
REVENUE SOURCE |
REVENUE AMOUNT |
|
Bond Proceeds |
|
|
Series A (6/98) |
$21,854,000 |
|
Series B (3/00) |
$46,300,077 |
|
BAN Funds (Series C, 10/00) |
$15,990,000 |
|
Series C (10/01) |
$110,171 |
|
Subtotal Bond Proceeds |
$84,254,248 |
|
Other Revenue |
|
|
Bond Interest |
$10,411,303 |
|
Bond Arbitrage Liability |
($419,412) |
|
BAN Interest |
$976,905 |
|
BAN Arbitrage Liability |
($210,905) |
|
Deferred Maintenance |
$974,499 |
|
Food Services |
$175,000 |
|
Capital Facilities Fund |
$2,597,047 |
|
State SB-50 Rel. 1 |
$1,906,616 |
|
State SB-50 Rel. 2 |
$26,514,241 |
|
SB-50 Interest |
$620,037 |
|
Grants |
$345,024 |
|
Donations |
$231,801 |
|
Insurance Reimb (Pool Deck) |
$122,748 |
|
Building Fund |
$19,814 |
|
General Fund |
$164,749 |
|
Subtotal Other Revenue |
$44,429,467 |
|
TOTAL REVENUE |
$128,683,715 |
Table 1. Revenue,
SCCS Bond Projects Budget,
Prior to the bond campaign, a Facility Assessment Team comprised of construction professionals and district staff evaluated each of the school sites, worked with site and district staff in developing a needs assessment, prioritized each site’s needs, and developed a cost estimate for needed and desired school construction projects. This facilities audit, along with community input, was used by the district to determine the amount of money that was requested in the bond election. Although approximately $130 million in needed and desired improvements were identified, a community survey indicated voters would be willing to support bonds totaling $86 million. Projects were prioritized based on the $86 million figure, and renovations and repairs addressing code requirements, health and safety concerns, and systems projects such as roofing, electrical, and plumbing were given priority.
After the election, district staff, together with architects
and construction managers, developed a Master Schedule to accomplish the
Facility Assessment projects. The schedule defined the sequence for planning
and construction of the projects at each school site from June 1999 through
December 2003. The schedule was discussed with all site principals and the Bond
Oversight Committee. Within the Master Schedule, each school site was listed
along with an anticipated planning and construction timeline. The work at each
school site was divided into the following tasks: pre-design, design, state
review, bidding, and construction.
In the “Road to Renovation” pamphlet mailed out by SCCS in May 2000 to residents within the SCCS boundaries, it was stated that the construction schedule called for all projects to be completed by the end of the 2003-2004 school year. Due to state funding and additional revenues, in May 2003, with SCCS Board approval, site planning committees began meeting to identify and prioritize additional modernization projects at each school site. As of June 2006, there are still three projects to be bid, and eighteen projects under construction. Projects may extend well beyond the end of 2006.
Bond projects were originally overseen by the Director of Bond Projects, a district administrative position, to provide general oversight and management of the program. Two architect/construction management teams (DES-WLC Architects/Turner Construction Management for the elementary schools, and Beverly Prior/Kitchell Construction Management for the secondary schools) assisted. Projects were put out to bid for multiple prime contractors, that is, a prime contractor for each trade. Due to the difficulty in managing multiple and separate contracts, missed work, and instances of poor work quality, the district discontinued its use of multiple prime contractors.
The bond projects are now managed by district staff and contracted firms. The organizational components for project management include:
· the Assistant Superintendent, Business Services, providing district administration oversight;
· general contractors bidding for projects;
· a construction management firm providing overall program management for bond projects (Strategic Construction Management);
· two architecture firms, one for the elementary and junior high schools (DES Architects), and one for the high schools (Beverly Prior Architects), providing design services and project administration;
· Inspectors of Record providing state-mandated site inspection services; and
· district employees (3.2 positions) paid by bond funds: a full-time district Construction Project Coordinator, a full-time clerical support person; a full-time accounting person; and support from the district purchasing manager for bidding and contracting processes.
In
“Responsible bidder,” as used in this part, means a bidder who has demonstrated the attribute of trustworthiness, as well as quality, fitness, capacity, and experience to satisfactorily perform the public works contract. (Section 1103)
On the day named in the public notice, the department shall publicly open the sealed bids and award the contracts to the lowest responsible bidders. (Section 10180)
SCCS District officials stated that the lowest, responsive,
responsible bidder is hired by the district. A responsive bidder is one that
has provided all necessary documents and meets all specified qualifications in
a timely manner.
When construction projects are put out to bid, a Request for Proposal (RFP) is published in the newspaper, and interested contractors are invited to submit bids by a specified date. On that date, the bids are publicly opened, recorded, and awarded to the lowest, responsive, responsible bidder.
The Division of the State Architect (DSA) reviews all
public school construction involving structural, fire/life safety, and
Once a project is completed, a Notice of Completion is
recorded at the
In Fall 1998, a committee consisting
of volunteer community members was formed by the district to provide oversight
for the bond projects. The Bond Oversight Committee (BOC) is an advisory body
only and makes recommendations to the school board. Final authority for all
aspects of the bond measures resides with the SCCS Board of Trustees. The BOC
meets every other month and receives reports on financial and construction
status; reviews standard bid documents and change orders; reviews contracts for
design, construction management, construction contractors, and contract
amendments; and has been involved in the reallocation of dollars between school
sites. Specified roles and responsibilities include attending all committee
meetings; becoming familiar with the laws, regulations, and processes that the
school district must satisfy in completing the projects authorized by the bond;
and working with all interested parties to facilitate communication about the
status of the bond projects.[6]
According to district officials, by the end of Summer 2006, ninety-eight percent (98%) of the bond funds
will have been spent as projects are nearing completion. The BOC’s final
meeting is scheduled for November 2006. A subcommittee has been established to
work with school district staff and Strategic Construction Management to
prepare a final report on the bond projects for the board and community
members, detailing how both time and money were spent under Measures E and H.
This investigation was undertaken to review financial documentation for the Santa Cruz City Schools Bond Measures E and H. The investigation included:
As the investigation progressed, the bond details and issues of project management, bidding, and oversight were also examined.
Santa Cruz City Schools District personnel.
Bond Oversight Committee members.
Division of the State Architect personnel.
Advantages/Disadvantages of Using Multiple Prime v. Single General
Contractor, agenda packet, Bond Oversight Committee meeting,
California
Department of General Services, Division of the State Architect, Project
Inspector Qualification Record, DSA-5, revised
Communications
Matrix for Bond Projects Participants,
IOR Bi-Monthly Progress Reports,
Memo from Northcross, Hill and Ach,
Official Statements, Santa Cruz City Elementary School District, General Obligation Bonds, Election of 1998, Series A, B, and C.
Official Statements, Santa Cruz City High School District, General Obligation Bonds, Election of 1998, Series A, B, and C.
Official
Statement,
Official Statement,
Santa Cruz
City Schools, Board of Education for the Elementary and Secondary Districts
Minutes,
Santa Cruz City School Bond Oversight Committee Meeting Minutes, May 16, 1998 to May 18, 2006. [Please see Appendix for specific dates.]
Santa Cruz City Schools “Bond Oversight
Committee Roles and Responsibilities,” revised
Santa Cruz City Schools Bond Project, Status
of Project Closeout,
Santa Cruz City Schools District Bond
Projects Status Reports,
Santa Cruz City Schools, Request for
Proposals, Management Services for Construction Projects, undated.
Contra
Costa Times, “Schools’ refinancing questioned,”
“Road to Renovation: Keeping You Informed,” Santa Cruz City Schools, undated.
“Bond-funded school repairs set to
start in
“Bonds making a difference,” March 22, 2001.
“Branciforte remodeling project
disappoints staff,”
“Error could cost schools thousands,”
“Firm will oversee school construction
projects,”
“Moving costs stir school-bond debate,”
“Santa Cruz City
Schools finds surplus in general fund,”
“Students say last goodbye to Natural
Bridges, Branciforte schools,”
Building Standards Commission, http://www.bsc.ca.gov.
California Code of Regulations, http://www.bsc.ca.gov/title_24/documents/part1/2001_part1.pdf.
California Education Code, http://caselaw.lp.findlaw.com/cacodes/edc/15200-15205.html.
California State Constitution, http://www.leginfo.ca.gov/const.html.
California Public Contract Code, http://www.aroundthecapitol.com/code/contents.html?sec=pcc.
“Choosing the Best Delivery Method for Your Facility Projects,” http://www.mbpce.com/news_pubs_delivery.html.
Division of the State Architect, http://www.dsa.dgs.ca.gov.
Division of the State Architect On-Line Project Tracking System, http://www.applications.dgs.ca.gov/dsa/etrackerweb/DistrictProject.asp?clientid=44-h2 and http://www.applications.dgs.ca.gov/dsa/etrackerweb/DistrictProject.asp?clientid=44-42.
General Obligation Bonds, http://www.calschools.com/static/GOBond.htm.
Santa Cruz City Schools, http://www.sccs.santacruz.k12.ca.us.
Santa Cruz County Office of Education, http://www.santacruz.k12.ca.us/board/index.html.
Santa Cruz Sentinel,
http://www.santacruzsentinel.com.
State Education Oversight Commissions, http://www.ecs.org/clearinghouse/57/86/5786.htm.
Strategic Construction Management, http://strategic-cm.com/main/santacruzcityschools.htm.
TBW&B, Public Finance Strategies, LLC, http://www.tbwb.com/clients.htm.
2001 California Building Standards Administrative Code, California Code of Regulations, Title 24, Part 1, http://www.bsc.ca.gov/title_24/documents/Part1/2001_part1.pdf.
Ten
1. The E and H bonds were originally each sold in three series: A, B, and C:[7]
|
Bond Sold |
Date |
Bond Amount |
Bond Term Ends |
|
Series A, Elementary |
|
$7,000,000.00 |
|
|
Series B, Elementary |
|
$15,500,000.00 |
|
|
Series C, Elementary |
October 2001 |
$5,598,115.65 |
|
|
TOTAL ELEM. |
|
$28,098,115.65 |
|
|
Series A, High School |
|
$15,000,000.00 |
|
|
Series B, High School |
|
$31,000,000.00 |
|
|
Series C, High School |
October 2001 |
$11,997,433.50 |
|
|
TOTAL HIGH SCH. |
|
$57,997,433.50 |
|
In April 2005, Series A and B Elementary and High School bonds were refinanced:
|
Refinance, Series A and B, Elementary |
April 2005 |
$22,785,000 |
|
|
Refinance, Series A and B, High School |
April 2005 |
$45,500,000 |
|
Table 2. Santa Cruz City Schools Bond Sales, Measures E and H.
2. Total Elementary bond sales, Series A, B, and C exceeded the $28 million dollar cap established in Bond Measure E.
3.
When asked about exceeding the $28 million cap on the
Elementary bonds, district administrative staff referred the
4.
The last of the original Elementary bonds was sold in
2001, but repayment of the $98,115.65 overage has not yet been made as of
5. When Elementary and High School Bonds, Series A and B were refinanced in April 2005, the total amount of the refunding bonds was $4,280,000 higher than the remaining principal of the original Series A and B bonds. The Elementary Series A and B Bonds were refinanced for $22,785,000 (the outstanding principal was $21,030,000); the High School Series A and B Bonds were refinanced for $45,500,000 (the outstanding principal was $42,975,000).[8]
6. SCCS District’s bond financial advisor stated that “the amount of the refunding bonds is determined by the amount needed to establish an escrow to pay off the old bonds, which includes interest and principal due . . . and pay the costs of issuance.”
7. Elementary bonds, Series C and Elementary 2005 Refunding Bonds total $28,383,115.65, again exceeding the $28 million cap established by the bond measure.
8.
The April 2005 refinancing of the Elementary and High
School Bonds, Series A and B is not detailed on the
SCCS Bond Projects Budget, Report from
9. According to the Official Statements for the bond sales, property owners residing in the Santa Cruz City Schools District will be repaying bonds E and H until 2029.
10. The
Voter Information Pamphlet for Bond Measures E and H contained an “impartial
analysis by
11. On
12. SCCS District’s bond financial advisor stated that the refunding of the bonds will result in lower debt service payments, with the majority of savings in 2006-2010, and that the refinancing will lower taxes.
13. For
tax year 2004-2005, property owners residing in the Santa Cruz City Schools
District within the City of
14. Interest earned on bond sale proceeds has been used for the bond projects and has not been used to repay the bond.[11]
15. As property tax is collected to repay bonds E and H, the money is deposited in the pooled investment fund of the county until the district draws it out. These deposits earn interest.
16. Following
is a summary of the SCCS Bond Projects Budget expenses from
|
ITEM |
EXPENSE |
PERCENTAGE OF EXPENSES |
|
Construction Contracts |
$82,431,328 |
74% |
|
Architects/Engineers |
$11,212,596 |
10% |
|
Construction Management |
$6,928,864 |
6% |
|
Miscellaneous Construction Costs |
$4,178,084 |
4% |
|
Reserves |
$3,901,483 |
4% |
|
Staff Salaries and Other Support |
$2,225,522 |
2% |
|
TOTAL EXPENSES |
$110,877,877 |
100% |
Table 3. Summary of
SCCS Bond Projects Budget Expenses,
17. In
January 2001, the Bond Projects staff requested authority from the school board
and the BOC to use their discretion before bidding projects in the future, and
to decide whether to bid projects with one general contractor or use
multiple-prime contractors.
18. Results
of the first four major bond projects undertaken at one high school, one junior
high school and two elementary were described as follows: “All four projects
were completed late, two of the four projects are over budget, the quality of
some of the work was sub-standard on two projects, and sub-standard work was
allowed to stand when first done, assuming it would be rectified as part of the
punch list at the end of the projects, but after many spaces had been
reoccupied. Some work that was planned to be included in some projects was left
out of the initial plans and specs and had to be added with change orders, adding
time and cost to the project.”[13]
19. At
the
·
bidding future construction projects using
general contractors
·
terminating the two elementary and secondary
Construction Managers’ contracts
·
increasing Inspector of Record time on projects
to better monitor quality of work
·
increasing architect involvement in construction
administration
·
reorganizing district support and oversight of
projects
·
pre-qualifying bidders for future projects
20. District
administrative staff stated that using general contractors had the advantages
of less contract administration, total coverage of work, and direct lines of
accountability. Disadvantages were that the general contractor might not select
the lowest subcontractor bid and could charge up to a fifteen percent markup on
subcontractor change orders.[14]
District administrative staff stated that using general contractors could cost
more, but there would be clear lines of responsibility and “headaches would be
reduced.”
21. On
22. Seven
firms responded to the district’s Request for Proposal (RFP) for a construction
program manager. Three finalists were interviewed, and Strategic Construction
Management was chosen by the SCCS Board as the Construction Program Manager to
be effective
23. The
district has not been able to produce the fixed-price bids and requested
supporting documentation for this selection process. This documentation is
public record.
24. The
25. “Previously,
the district used its staff to oversee multiple contractors at individual
schools. Officials expect the new system, which includes hiring a general
contractor for each project, will simplify the process and attract more bids,
particularly from area contractors. The district will pay Strategic $1.2
million. District officials expect to finish all projects by December 2004.”[17]
26. Construction
Management budgets were reduced by $2,128,663 due to termination of the two
previous Construction Management contracts. Architect Fee budgets were then
increased $1,288,160 for increased services for construction administration due
to reorganization of management for the projects. These adjustments, when
combined with the new Strategic Construction Management contract for $1.2
million, produced an immediate overall increase for the bond projects of over
$360,000.
27. Since
February 1, 2002, there have been numerous contract extensions and additional
payments approved for Strategic Construction Management, summarized as follows:
|
|
Original Contract[18] |
Moving Services[19] |
Contract Renewal[20] |
Contract Extension[21] |
Moving Contract[22] |
Contract Extension[23] |
TOTAL |
|
Term |
|
|
|
|
5/05 – 9/05 |
|
|
|
Amount |
$1,205,104 |
$99,825 |
$958,058 |
$374,325 |
$27,254 |
$224,500 |
$2,889,066 |
Table 4. Approved
Contracts for Strategic Construction Management Paid by Bond Funds.
28. In
addition to bond funds, payments totaling $68,273 to Strategic Construction
Management have been approved by the SCCS Board: $48,221 from the General Fund
to “plan and coordinate moving of furniture, equipment and supplies (March 24,
2004); and $20,052 from the Capital Facilities Fund to “plan and coordinate the
relocation of 21 portable classrooms” (April 21, 2004).
29. In
the RFP for Management Services for Construction Projects that was part of the
Strategic Construction Management Agreement with the district, one requirement
is to “plan and coordinate the moving of staff, furniture, material and
equipment related to the construction projects.” Strategic Construction
Management submitted a fixed fee proposal to secure this contract.
30. In
March 2002, the board approved a district Construction Projects Coordinator
position to serve as a liaison between Strategic Construction Management and
the district sites. The position is funded through the elementary and secondary
bonds. The head of the district Maintenance Department was appointed to the
position.
31.
The SCCS Board of
Education approved a resolution to no longer require a public re-bidding of
work once change orders exceeded the cost of the original bid by over ten
percent (10%), as had been previously required. It was stated that the re-bid
process can cause a six- to eight-week delay, and since the district had a
general contractor in charge of bond-funded projects, the chances of exceeding
a ten percent overrun were considerably less.
32.
The SCCS Bond Project, Status of Project Closeout,
33.
In October 2005,
the SCCS Board voted to become subject to the Uniform Public Construction Cost
Accounting Procedures and to provide for informal bidding procedures under the
Uniform Public Construction Cost Accounting Act Procedures. This allowed
projects from $35,000 to $125,000 to be bid using a pre-approved list of
satisfactory contractors, while projects over $125,000 were subject to formal
bidding procedures. The rationale was that this would allow more flexibility in
the execution of work; speed up bidding procedures; improve timeliness of
project completion; reduce paperwork and expenses related to advertising; and
simplify administration.
34.
The SCCS District
was advised by legal counsel to set a consistent policy for the acceptance of
bids. Subsequently, it was decided to award contracts based on the lowest total
bid on each project. Projects often contain several alternates, which may or
may not be actually included in the final project. The contract, however, is
still awarded on the total bid.
35.
When projects
contain alternates, contractors can bid low or even zero (0) on some
alternates, thereby lowering their overall total bid.
36.
In March 2006, the
district awarded a bond project contract to a bidder whose past projects for
the district included a project that had change orders totaling 34.1% of the
original contact amount, a Stop Notice, and had gone to court. That same bidder
had previously completed district bond projects with change orders of 32.3%,
36.9%, and 118.8% of the original contract amounts.
37.
Contracts were not
always awarded to the lowest bidder as evidenced by Bid # 2006-09. The contract
was awarded for $1,204,700 when the lowest bid was actually $1,151,399.
38.
The SCCS Bond Project, Status of Project Closeout,
39.
The SCCS, Bond Project, Status of Project Closeout,
40.
Sixty-nine completed or nearly-completed projects
detailed on the SCCS, Bond Project, Status of Project Closeout,
41. District officials stated that general contractors typically make a fifteen-percent markup on change orders.
42.
According to the
43.
The
44. Inspector of Record assignment date records obtained from the SCCS District and the DSA do not match.
45. “The school board must provide for and require competent, adequate and continuous inspection by an inspector . . .” and; “The project inspector . . . must be approved by the DSA for each individual project.”[25]
46.
In reviewing
the IOR field reports for Santa Cruz High Modernization, project number
01-103363, there is a gap of eighteen days with no IOR reports or notations.
One inspector had been terminated on
47.
DSA Field Notes
from the supervising field engineer from
48.
In January 2001, the BOC questioned the prudence of
using bond funds to modernize schools that might be closed in the future due to
declining enrollment.
49.
In June 2004,
|
LEASE REVENUES |
|||||
|
|
04-05 |
05-06 |
06-07 |
07-08 |
08-09 |
|
Natural Bridges |
$68,000 |
$83,232 |
$84,897 |
$86,595 |
$88,326 |
|
Loma Prieta |
$140,000 |
$165,000 |
$200,000 |
$228,400 |
$275,500 |
|
|
$208,000 |
$248,232 |
$284,897 |
$314,995 |
$363,826 |
Table 5. Santa Cruz
City Schools Lease Revenues, 2004-2009.
50.
In August 2004, a citizen who attended two BOC meetings
expressed concern about bond funds that had been used on schools that were
later closed. The citizen felt that the lease money from those schools should
be used to reduce the bond debt.
51.
District administrative staff reported to the BOC
committee that legal counsel said it was not illegal to lease out the renovated
schools and not use the revenues to defray the debt. The BOC approved a motion to not recommend using lease revenues to
retire bond debt.
52.
Even after
53.
Classrooms identified to house the district offices at
Soquel High had already been remodeled using bond funds. At least an additional
$460,537 in bond money was spent for the district office remodel.
54.
At its
55.
To date, at least $1,285,486 of bond project money has
been spent on district office and adult education relocation. This total
includes $274,424 for change orders, or twenty-seven (27%) of the original
contract amount of $1,011,062.
56.
A BOC member called the use of bond money for offices
“not ethical,” and stated that the district could use anticipated redevelopment
revenue to pay for the classroom conversions and other relocation projects.
“There was a promise (the bond money) would never be used for administrative
costs. It was to improve the student environment, not the district office
environment.”[28]
57.
The BOC has been meeting bi-monthly since 1998. These
meetings are open to the public. Minutes and any reports released are public
information. Meetings are held at
58.
In 1998, a bond web page was developed with links to
each school site providing regular updates on bond-related issues.
59.
In June 1999, the communications sub-committee of the
BOC worked on placing bond-related information on the SCCS web page. Signs
relating to bond projects were designed for placement at the school sites.
60.
On
61.
District staff and BOC members were interviewed for
“Community Express,” a Community Television of Santa Cruz show. The show aired
four times in Fall 1999 and outlined the school bond
issues and future project plans.
62.
A brochure “The Road to Renovation” detailed the status
of Measure E and H projects and was distributed to parents from the school
sites and mailed to households within the district in May 2000. This brochure
indicated there would be ongoing communication to keep the public aware of
progress and improvements.
63.
In July 2000, a Board of Education member noted that
the district’s web site was in need of updating.
64.
The
65.
When asked about the inaccessibility of the web site,
district staff responded that the webmaster worked one half-day per week and
that there were no resources in the district to put more effort into the web
site.
66.
Strategic Construction Management publishes SCCS site
construction newsletters on its web site. Newsletters for completed bond
projects include construction budget summaries, schedules, and architect,
inspector, and contractor information. Web site summaries of current projects
have none of this information.[29]
67.
The construction budget summaries for “Completed
Projects” on the Strategic Construction Management web site do not match the
figures printed on the Santa Cruz City
Schools Bond Project, Status of Project Closeout, May10, 2006. The Strategic
Construction Management web site is the only one displaying information on the
SCCS bond construction projects.
68.
According to district administrative staff, by the end
of summer 2006, ninety-eight percent (98%) of bond funds will be spent. The
BOC’s final meeting is scheduled for November 2006. If there is any money left
over, district staff will oversee expenditures. Construction projects could
extend into Spring 2007.
69.
Strategic Construction Management will be paid $34,500
to produce a Bond Projects Report. This fee is included in their
70.
At its
1. Measure E, Series A, B, and C bond sales
exceeded the voter-approved amount of $28 million by $98,115.65. The $28
million cap was exceeded a second time when the Measure E, Series A and B bonds
were refinanced, this time by $383,115.65.
2. A savings of over $3 million in interest is
projected due to the refinancing of the Elementary and High School Bonds,
Series A and B that were sold for $4,280,000 million more than the principal
remaining. Although interest was decreased, the total debt was increased. The
purpose of the refinancing appears to be to extract more funds and not to lower
property taxes.
3. The 2005 refinancing of the Elementary and
High School Bonds is not shown on the SCCS Bond Projects Budget, Report from
4. Contrary to the language of the Voter
Information Pamphlet, the bond terms of both the Elementary and High School
bonds are greater than twenty-five years.
5. Property owners in the Santa Cruz City
Schools District are paying a higher percentage of their property taxes to
repay bonds E and H in the 2005-2006 tax year than
they paid in the 2004-2005 tax year. To date, the decreased bond interest rates
have not reduced property taxes.
6. Over the next twenty-three years, property
tax deposits will earn interest that could be used to reduce bond debt.
7. The SCCS District has exceeded its fiscal
authority granted in Measures E and H by selling bonds for more than the
voter-approved limit. By so doing, it could make it more difficult for voters
to approve future bond projects.
8. As of
9. The district did not have personnel on staff
with adequate construction knowledge to manage large construction projects.
10. The district could not find an efficient and
cost-effective method of construction program management. There were many
layers of construction supervision and coordination paid for with bond dollars:
general contractors, architects, Strategic Construction Management, and the
district’s Construction Program Coordinator.
11. Originally, the Strategic Construction
Management contract was for $1.2 million and all projects were to be completed
by December 2004. By the end of 2006, payments to Strategic Construction
Management will reach nearly $3 million, and projects are still continuing.
12. Additional payments were made to Strategic
Construction Management for moving services that were part of their original
contract with SCCS for which a fixed-price bid had been submitted.
13. Total bond project construction management
fees from 1998 to present appear excessive, and will top $7 million before the
end of 2006.
14. The bidding process for the Construction
Program Manager was not conducted according to Public Contract Code Procedures.
Bid documentation is not available from the district to determine whether the
lowest bidder was accepted; and documentation that the bids were opened in
public as mandated by the Public Contract Code has not been made available by
the district.
15. When the board voted to no longer require
re-bidding projects that surpassed the ten percent change order threshold, it
removed the cap on change orders.
16. A contractor should not have been considered
“responsible” if that contractor’s previous jobs had excessive change orders
and if court action was necessary.
17. When projects were bid with alternates, this
allowed contractors to manipulate the system by giving a low bid or zero on
alternates, thereby allowing a contractor to submit the lowest bid. The bid
would not necessarily be awarded to a responsible bidder.
18. The SCCS Bond Project, Status of Project Closeout,
19. The amount of change orders appears
excessive. This could be due, in part, to the removal of the ten percent (10%)
cap requiring project re-bidding.
20. There was no financial incentive for
contractors and architects to keep change orders to a minimum.
21. The Architects of Record have not fulfilled
their responsibilities to secure project closeout and certification by the DSA.
22. District administrative staff has not seen
the projects through to closeout by insisting that the Architects of Record
submit all closeout documentation.
23. The district, architect, and engineer failed
to file DSA Form-5 before IORs started project
01-103363 as required by the California Code of Regulations.
24. IOR documentation for project 01-103363 is
incomplete and shows a gap of eighteen days with no IOR site notations or
reports. It is a violation of the California Code of Regulations for a project
to proceed without an IOR.
25. Since district and DSA documentation of IOR
assignments and dates do not match, the
26. Although bond funds were used to renovate the
27. Despite the fact that the Voter Information
Pamphlet arguments in favor of the bond measures clearly stated that bond funds
were not to be used for administrative offices, the SCCS Board used bond funds
for this purpose.
28. The SCCS Board ignored BOC recommendations
not to use bond funds for district office renovations and relocation.
29. Lack of planning resulted in wasted money at
Soquel High when ten classrooms that had already undergone renovation and
modernization were remodeled for district offices.
30. The SCCS District spent more than $1.2
million on district office renovations and relocations. The district
inappropriately approved $1 million for this purpose; no bond money should have
been used.
31. The BOC is scheduled to disband in November
2006. Projects may continue until at least Spring
2007, and there will be no BOC oversight. Bonds were passed under the
assumption that an oversight committee would be in place for the duration of
the projects.
32. The district has not maintained the bond
project information on its web site. This could have been a valuable means of
providing ongoing, up-to-date public information on the bond projects.
33. Over the last eight years, there has been no
ongoing form of public communication with district residents regarding the bond
projects. Efforts made, such as starting a web page, being interviewed for
Santa Cruz Community Television, and producing a brochure, all took place between 1998-2000.
34. As of this late date, the BOC has not yet
determined the format and scope of its final report. The
35. Paying
Strategic Construction Management $34,500 to help prepare a final report
detailing the bond projects could result in a loss of objectivity and detail in
evaluating the projects’ successes and failures.
1.
The
2. An outside, independent performance audit should be conducted to analyze, assess, and report on the Santa Cruz City Schools District’s operational and construction management policies, procedures, and practices regarding Bond Measures E and H. Investigation as to whether all California Code of Regulations, Title 24 standards were followed should be included.
3. The SCCS District should insist that the architects submit all documents related to completed bond projects under DSA supervision so the projects can be certified and closed out. Architect fees should be withheld until DSA certification is complete.
4. For future major construction projects, the SCCS District should consider hiring an experienced, qualified construction project manager or team as a limited-term district employee(s). This would cost less than hiring a construction management firm.
5. The SCCS District should replace the funds used for District Office relocation and renovation to reduce bond debt.
6. The SCCS District should use lease revenues and interest on future property tax collections to reduce the bond debt.
7. The SCCS District should provide a complete bond projects budget document that includes bond refinancing details.
8. The SCCS District should provide a complete bond projects closeout document detailing all bond construction projects.
9. Future construction projects should be awarded to the contractor submitting the lowest base bid. Alternates should be bid separately.
10. For future construction projects, the contractors hired should adhere to the ten-percent cap on change orders previously in effect.
11. The SCCS District should provide an objective summary and analysis of bond projects from beginning to end. This should include project details, budget, and completion dates; financial accounting; analysis of successes and failures; and suggestions for improvement for any future bond or construction projects.
12. The SCCS District should make sure its web site is comprehensive and updated frequently. The final bond projects report and analysis should be posted on that web site.
13. The BOC should continue to operate until all bond projects are completed.
14. District support staff is to be commended for its helpfulness, promptness, and courtesy when providing requested documentation.
Entity |
Findings |
Recommendations |
Respond Within |
|
Santa Cruz City Schools Board of Trustees |
2-12, 14, 15, 19, 20, 23, 24, 27-29, 31, 32, 34-44, 46, 47, 51, 53-56, 64-70 |
1-13 |
90 Days ( |
|
|
1-15 |
1 |
60 Days ( |
Appendix A – Source Details
Santa Cruz City Schools, Board of Education for the Elementary and Secondary Districts Minutes:
Santa Cruz City Schools Bond Oversight Committee Meeting Minutes:









[1]
[2]
[3] Figures
supplied by the Santa Cruz County Auditor/Controller Office,
[4]
[5] California Public Contract Code, http://www.aroundthecapitol.com/code/contents.html?sec=pcc.
[6] Santa
Cruz City Schools, “Bond Oversight Committee Roles and Responsibilities,”
revised
[7] Official Statements, Santa Cruz City Elementary School District, General Obligation Bonds, Election of 1998, Series A, B, and C; Official Statements, Santa Cruz City High School District, General Obligation Bonds, Election of 1998, Series A, B, C; Official Statement, Santa Cruz City Elementary School District, 2005 General Obligation Refunding Bonds; Official Statement, Santa Cruz City High School District, 2005 General Obligation Refunding Bonds.
[8] Official Statement, Santa Cruz City Elementary School District, 2005 General Obligation Refunding Bonds; Official Statement, Santa Cruz City High School District, 2005 General Obligation Refunding Bonds.
[9]
[10] California Education Code, Section 15144, http://caselaw.lp.findlaw.com/cacodes/edc.html.
[11]
[12]
[13]
[14] “Advantages/Disadvantages of Using Multiple Prime v. Single General
Contractor, agenda packet, Bond Oversight Committee meeting,
[15]
[16] California Public Contract Code, Section 10180, http://www.aroundthecapitol.com/code/contents.html?sec=pcc
[17]
[18] Santa
Cruz City Schools, Board of Education for the Elementary and Secondary
Districts Minutes,
[19] Santa
Cruz City Schools, Board of Education for the Elementary and Secondary
Districts Minutes,
[20] Santa
Cruz City Schools, Board of Education for the Elementary and Secondary
Districts Minutes,
[21] Santa
Cruz City Schools, Board of Education for the Elementary and Secondary
Districts Minutes,
[22] Santa
Cruz City Schools, Board of Education for the Elementary and Secondary
Districts Minutes,
[23] Santa
Cruz City Schools, Board of Education for the Elementary and Secondary
Districts Minutes,
[24] 2001
California Building Standards Administrative Code, California Code of
Regulations, Title 24,
Part 1, Sections 4-339 and 4-341, http://www.bsc.ca.gov/title_24/documents/Part1/2001_part1.pdf.
[25] 2001
Part 1, Section 4-333(b).
[26] California Department of General Services, Division of the State Architect, Project Inspector Qualification Record, DSA-5, revised, March 27, 2003.
[27] Agenda Packet,
[28]
[29] Strategic Construction Management, http://strategic-cm.com/main/santacruzcityschools.htm.